On March 4, Start Early along with our partners at Child Care For All, COFI, Evanston Early Childhood Council, Illinois Action for Children, Raising Illinois, SEIU, and We, the Village brought over 300 advocates down to Springfield to advocate for Illinois’ youngest learners. Advocates shared their perspectives with legislators on the impact that increased funding for the Early Childhood Block Grant, ECACE, child care, home visiting and Early Intervention would have on Illinois families and providers.
The spring legislative session will continue through May 31, and we aren’t slowing down our advocacy efforts! Here’s how you can still participate:
- Contact your legislators
- If you weren’t able to join the live webinar, the recording of the Advocacy 101 training hosted by our partners at Illinois Action for Children is a great resource for getting more comfortable communicating with legislators
- Use our social toolkit to share more about the impact of increased early childhood funding with your personal networks
- Share your Early Intervention story
- To keep up with the work of the Illinois Policy Team you can also follow along on Twitter: @EarlyEdIL
More Like This
Stay Connected
Stay up to date on early childhood policy issues and how you can take action to ensure more children have access to quality early learning and care in Illinois.
Illinois Policy & Advocacy
For decades, our policy team has been a leading voice and advocate for early learning and care in Illinois.
Contact Us
Connect with our team to learn more about our work or discuss how we can support policy and advocacy work for your organization.
Earlier this month, I had the opportunity to join advocates, home visitors, program leaders, public sector leaders, funders, and researchers at the 2025 National Home Visiting Summit in D.C. I was inspired by the diverse, cross-disciplinary group who shared ideas, built community, and learned and reflected with each other on how we can continue to build high-quality home visiting services, structures, and systems.
In those discussions, I heard several themes around how state and local public sector leaders and advocates can continue to strengthen home visiting systems to better serve children and families.
- Address workforce challenges by working across sectors and agencies. While policymakers often discuss workforce shortages at a system level, programs still often feel that they must generate the solutions on their own. Speakers at the Summit offered many potential solutions to address workforce challenges in effective, cross-sector ways. For example, state MIECHV administrators are partnering with Early Intervention/Part C coordinators to build relationships and workforce capabilities through shared professional development. Deploying the same professional development to build reflective supervision capacity across an entire state can benefit not only home visitors, but Early Interventionists, early educators, and others. In addition, counties are collaborating regionally to provide mental health supports for home visitors across models.
- Leverage diverse funding streams to support home visiting. As states seek to expand home visiting services and build more comprehensive, coordinated systems to support children and families, they need new strategies to increase funding and support sustainability. In addition to the two sources traditionally used to fund home visiting – MIECHV and Early Head Start – state systems leaders are leveraging other funding streams, including Temporary Assistance to Needy Families (TANF), Title I of the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA), the Preschool Development Grant Birth through Five (PDG B-5), Medicaid, and private insurance. In Oregon, state system leaders are using a combination of state general funds, Medicaid, and private health insurance to fund Family Connects statewide (Universal Newborn Support Services or UNSS). Also, in Colorado, the Tri-County Health Department (TCHD) leverages TANF funds to support home visiting services through their Nurse Support Program and Brief Parenting Program.
- Center the voices of families and providers for a demonstrated positive impact in systems building. State and local system leaders are challenging old mindsets and creating new infrastructure to place families and home visiting professionals at the center of decision-making in policy, practice, and research. When they do so, they find that the insights, suggestions, and buy-in generated helps drive strong outcomes for children and families. For example, state leaders scaling Family Connects (a universal postpartum short term home visiting approach) in New Jersey surveyed nurses to determine what makes the nurse home visiting role particularly attractive. Based on the results of that survey, they have built new supports and features in competitive requests for proposals and partnered with nursing schools to offer service-commitment scholarships. Additionally, the Seeds of Success program in Washington includes parents as board members and partnered with them to design a more collaborative approach to trauma-informed home visiting services.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive noteworthy developments in state and federal early childhood news, policy trends and stories highlighting work across our network.
Do any of these themes resonate with you and your home visiting system?
- For support strengthening your home visiting or other early childhood system, reach out to our Consulting Team at Consulting@StartEarly.org.
- To join the conversation, sign-up for our home visiting Policy & Advocacy Community of Practice.
- To get more policy-related information and insights in your inbox, sign-up for our Policy Perspectives newsletter.
More Like This
Our Policy Work
We work at local, state and federal levels to create effective, inclusive and interconnected educational opportunities for our youngest learners.
The National Home Visiting Summit
Our annual conference brings together early childhood leaders to advance the home visiting field.
At Start Early, we know that reading is fundamental to a child’s development. As we celebrate Read Across America Day, we recognize the importance of making reading with your little ones a priority every day! By reading with your young child, you are not only bonding and inspiring a love of reading, but also developing strong early language and literacy skills that are key to future learning and success.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive news, helpful tools and learn about how you can help our youngest learners.
No matter how old your child is — from babies and toddlers to preschoolers — these six tips from our experts will help you make the most of storytime:
- Start early. Reading to babies is important for healthy brain development and lays the foundation for language and writing skills.
- Make reading a part of your daily routine. Establishing a routine helps ensure that reading is part of your daily schedule, such as before naptime and bedtime. It also creates times during the day that both of you can look forward to.
- Try board and cloth books for babies. By age 1, most babies can grab books. Board and cloth books are great options for babies who like to touch things and put everything in their mouths.
- Take turns with your toddler. By age 2, most toddlers can hold a book and point at the pictures. Let your toddler turn the pages of a board book, and respond when they point or react to the story.
- Ask your child questions. As you read to your child, make the experience interactive by asking questions, such as “What do you think will happen next?” or “What was your favorite part of the story? Why?”
- Just keep reading. Reading to your child helps them develop a habit of listening to stories and loving books. This is one of the most important pieces of advice – make sure you are reading early and often.
One of the most important aspects of building early literacy skills is for parents to read to their young children. Through sharing these moments of being together and parents showing their genuine love for reading, children also get excited for reading which sets the foundation for building lifelong literacy skills.
Danielle Jordan, Senior Master Teacher, Educare Chicago
See our expert in action!
Check out how Educare Chicago Senior Master Teacher Danielle leads her class in a lesson on perspective and how you can tell the same story
in different ways.
Families living in communities that are under-resourced lack access to the quality early learning and care programs that help level the playing field and close the opportunity gap. With your support, we can provide literacy support for families in greatest need.
 Whether your child is a newborn or about to head to kindergarten, here are some great books to read during storytime:
Whether your child is a newborn or about to head to kindergarten, here are some great books to read during storytime:
- Little Blue Truck by Alice Schertle
- Giraffes Can’t Dance by Giles Andreae
- Smile, Baby Faces Board Book by Roberta Grobel Intrater
- Hair Love by Matthew A. Cherry
- Peekaboo Morning by Rachel Isadora
- We’re Different, We’re the Same by Bobbi Kates
- Don’t Let the Pigeon Stay Up Late by Mo Willems
- Grumpy Monkey by Suzanne Lang and Max Lang
- What If by Samantha Berger
- Swimmy by Leo Lionni
- The Day the Crayons Quit by Drew Daywalt
Other Early Learning Resources:
Why Early Childhood
Quality early childhood is one of the best ways to level the playing field. Learn why and about the impact we’re having.
Support Our Work
Together, when we start early, we can close the opportunity gap and ensure every child has a chance to reach their full potential.
Resources for Families
Discover educational activities and resources from Start Early experts to provide easy and engaging educational experiences with your child.

An Empty and Quiet Legislative Building… For Now!
(Photo Courtesy: Erica Hallock)
Trivia!
This week we are talking license plates! Hang with me, it’s actually rather interesting…
Other than commemorating special occasions, in what year did Washington state begin issuing specialty license plates? Bonus question: What was the subject of the first specialty plate?
Highlights of the Week
Governor Ferguson – Budget Reduction Exercises
On February 27, Governor Bob Ferguson held a press availability to preview a recommended $4 billion in savings and efficiencies to help address the state’s budget crisis. His approach is summarized in this press release. These reductions would be in addition to the approximately $3 billion in savings proposed in Governor Inslee’s “Book Two” budget.
Before I get to the specific early learning items Governor Ferguson proposed, here are some take-aways from his press conference:
- The actual amount of the four-year budget shortfall varies depending on who you ask. In his press availability today, Governor Ferguson stated his administration is assuming a $15 billion shortfall over four years.
- Governor Ferguson’s recommendations are based on potential savings identified by state agencies. The Governor’s recommendations do not include every agency identified savings opportunity. Governor Ferguson said state agencies identified about $1 billion more in potential savings that he is not advancing to the Legislature for their consideration. Each agency’s suggested reduction list will be posted on the Office of Financial Management website by February 28. We will report on these in next week’s Notes from Olympia.
- Not surprisingly, right out of the gate the press asked the Governor about his appetite for new revenue. He replied that it is still too soon to consider revenue from his perspective. He also said the state is not in a position to tax its way out of its budget hole.
- Governor Ferguson acknowledged his team did not have sufficient time to perform a thorough review of the full budget. He also recognized the upcoming March 18 Revenue Forecast could change the budget outlook for the better, or the worse.
- Governor Ferguson proposes funding Collective Bargaining Agreements with state employees but he also suggests a $300 million savings by instituting a one-day a month furlough for state employees for a two-year period.
Governor Ferguson released a 152-page document detailing potential savings. Related to early learning, the Governor proposes a total of $254.8 million in savings for DCYF in the following areas:
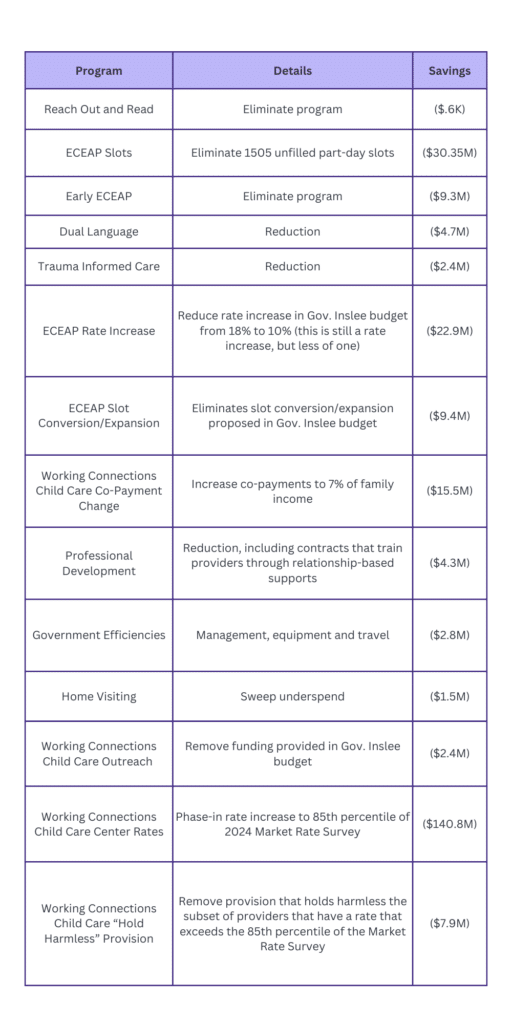
A Busy Week of Fiscal Committee Meetings Before Today’s Fiscal Cutoff
The focus of week seven was almost exclusively on fiscal committees in advance of the Friday, February 28 fiscal committee cutoff. With the state’s budget shortfall, it was not uncommon to see bills get scheduled – and then unscheduled – for hearings or executive sessions. We also saw adoption of a number of amendments as bill sponsors and advocates worked to reduce the costs of bills to keep them moving.
Each Thursday, Start Early Washington updates its bill tracker with the latest information on bills we are following. As we reach each cutoff, we transfer the bills that are not “moving” into a separate chart below to make the active bills easier to identify.
Below we have included updates on key early learning bills. Please note that with fiscal cutoff scheduled after the release of this newsletter, it’s a good idea to check the legislative website for the latest information.
Changes to Fair Start for Kids Act Advance
On February 25, the Senate Ways and Means Committee held a public hearing on SB 5752 (C. Wilson) which would modify many aspects of the Fair Start for Kids Act. You can watch the hearing beginning at 3:18 on TVW.
The real-world impacts of the legislation were noted in this week’s Democratic Media Availability in opening comments by Senate Majority Leader Jamie Pedersen who referenced this particular bill hearing and the “wrenching testimony from the real human beings who are going to be affected by the cuts we are likely going to have to make…”
The fiscal note prepared for the bill assumes $332.5 million in savings for the 2025-27 biennium and $547.6 million in savings for the 2027-29 biennium as well as additional indeterminate savings. (The fiscal note was prepared prior to the amendments adopted in the Senate Ways and Means Committee on February 27, so those changes are not reflected in the fiscal note). Fiscal notes are an estimate of the fiscal impact of a bill prepared by the relevant state agency and approved by the Office of Financial Management.
On February 27, the Senate Ways and Means Committee took executive action to approve SB 5752 with amendments.
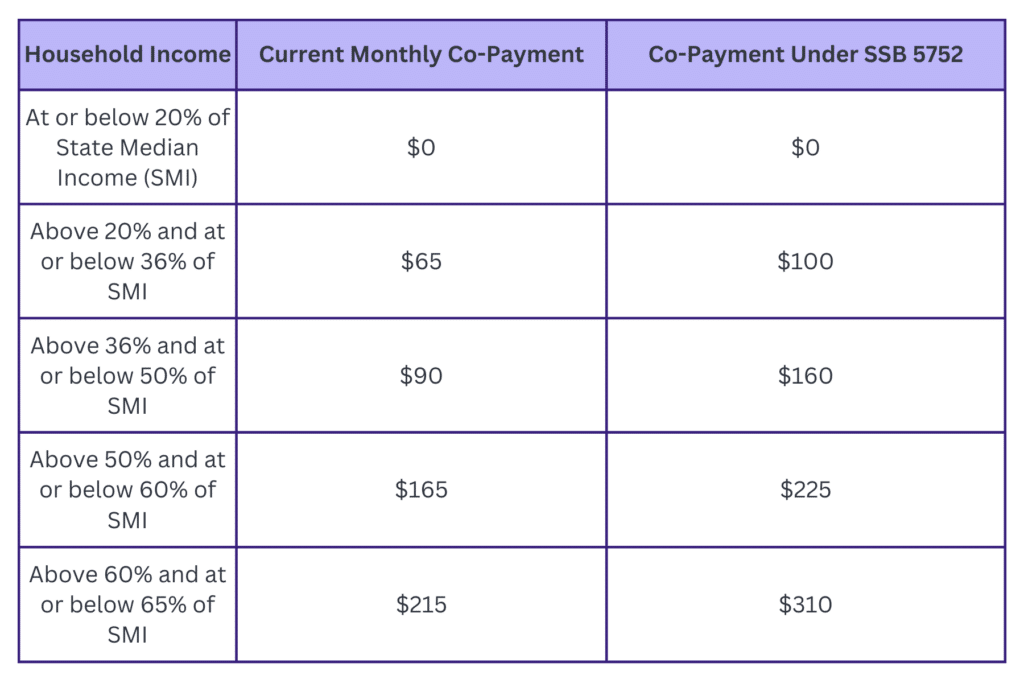
The substantive parts of the amendments relate to co-payments, setting in place a new family co-payment schedule effective October 1, 2025, through September 30, 2026, to be replaced by a per child co-payment schedule effective October 1, 2026.
These changes to co-payments apply to new applicants and re-applicants for subsidies. We believe this means a family’s co-payment would not change in the middle of their 12-month authorization. Additionally, student parents and children participating in Working Connections Child Care as a result of their engagement in Child Protective Services would not have a co-payment.
Following are the new co-payment structures:
Family Co-Payment Structure
Effective October 1, 2025 – September 30, 2026
Per Child Co-Payment Structure
Effective October 1, 2026
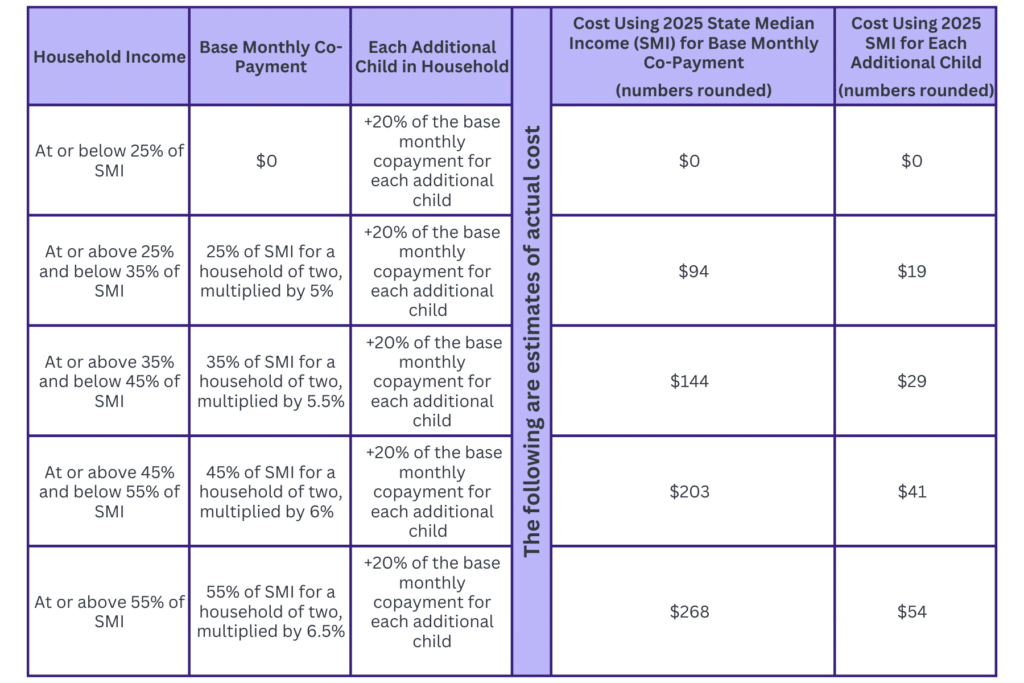
For information on the underlying bill details, refer to the February 14 Notes from Olympia. Be sure to note the amended co-payment approach above replaces what was included in the original bill.
The bill now moves to Senate Rules.
New Transition to Kindergarten Bills Introduced
This week, two new bills were introduced related to Transition to Kindergarten, HB 2012 (Bergquist) and SB 5769 (Wellman).
Both bills seek to pause the growth of the Transition to Kindergarten (TTK) program in slightly different ways. HB 2012 limits TTK program enrollment for each school district, charter school or state-tribal education compact school to its 2024-25 school year enrollment, beginning in the 2025-26 school year. SB 5769 limits Transition to Kindergarten Program funding beginning in the 2025-26 school year to the threshold set by enrollment during the 2024-25 school year.
SB 5769 received a public hearing in the Senate Ways and Means Committee on February 27 and, at the date of this writing, was scheduled for executive session on February 28. HB 2012 was referred to the House Appropriations Committee but has not received a hearing as of this writing. The other TTK bill, SHB 1450 (Santos), has also been referred to House Appropriations and has also not been scheduled for a hearing. We can presume these bills are all “NTIB,” or Necessary to Implement the Budget.
Provider Qualifications Bill Passes Fiscal Committee
On February 26, the House Appropriations Committee took executive action to approve SHB 1648 (Dent), as amended in committee. The amendment requires DCYF to convene the required stakeholder group and produce the directed report within existing resources.
The bill now moves to the House Rules Committee.
It’s Official – it’s Secretary Senn!
On Tuesday, February 25, the Senate unanimously voted to confirm Tana Senn as the second official Secretary of the Department of Children, Youth and Families. Congratulations, Secretary Senn!
What’s on Deck for Next Week
On the Floor Again…
Like clockwork, following fiscal committee cutoff, activity on the Capitol campus will shift to the Legislative building as lawmakers will debate bills that have made it to the floor in their respective house of origin prior to the next cutoff date of March 12 – aptly named the House of Origin Cutoff.
During floor activity, there are typically few committee hearings and legislators tend to spend a lot of time in their party caucuses being briefed on bill details and preparing for floor debate. Lobbyists spend hours on end on the “3rd floor” desperate for their priority bills to be approved (or defeated) so they can leave the circus.
Trivia Answer
Washington state’s first specialty plate was issued in 1997 honoring Washington State University. I was unable to find out how long it took for the University of Washington to secure its own specialty plate after WSU paved the way.

This week’s trivia was inspired by a February 19 Washington State Standard article highlighting debate over whether the state should slow down efforts to initiate new specialty license plates.
As background, HB 1368 (Orcutt) is an omnibus bill that would “green light” seven new license plates: 1) Keep Washington Evergreen; 2) LeMay-America’s Car Museum; 3) Mount St. Helens; 4) Nautical Northwest; 5) Smokey the Bear; 6) the State sport (pickleball); and 7) Working Forests. These are all potential plates that have been in the pipeline, so passage of this omnibus bill would get them over the finish line and make them available for motor vehicles in our state.
Rep. Donaghy (a proponent of the Smokey the Bear plate) sponsored HB 1952 which would ban new license plates (after the aforementioned seven go through) to provide time to review the specialty license plate process, including the identification of ways for the state to recoup costs for plates that are less popular with the public.
As the picture below proves, my childhood hero Smokey the Bear was on campus last week. He did not speak, but I think he was doing some subtle lobbying for passage of his plate.

Side note: Check out the construction going on at the Prichard Library
(Photo courtesy: Smokey’s Handlers)
So, the combination of the Washington State Standard article and my chance meeting with Smokey the Bear put me on a search to learn more about specialty license plates in Washington state. And, as I was on my search, I learned a lot about the evolution of license plates in our state. Learnings I must pass along…
1905
- Following the development of motor vehicles, the Department of Motor Vehicles was created under the Secretary of State. In the early years, the Secretary of State personally signed each vehicle license.
- In the first year, 763 vehicle licenses were issued at $2 each, bringing in $1,526 in revenue to the state.
- Vehicle licenses were originally issued to the person and not the vehicle. It was the individual’s responsibility to figure out how to affix the license plate to the vehicle.
1921
- A law passed that every existing license plate in the state would expire on December 31st. This led to the need to reorder license plates for every vehicle in the state. When the plates arrived, they were stored in the basement of the Old Capitol Building (the building that now houses the Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction). The plates were so heavy they caused the floors to sink, so the license plates had to be redistributed throughout the building over a weekend.
1923
- License plates began to be produced by inmates through the Department of Corrections. This practice continues to this day, and most are produced by inmates at the Walla Walla State Penitentiary.
1926
- The name of our state was listed as “WN” on the license plate. People were very disturbed by this abbreviation, finding it quite undignified and not a proper representation of our fine state, particularly when traveling to other parts of the country. Finally, in 1926, the full name of the state was spelled out. I was surprised to learn that the appearance of a state license plate could illicit such a strong public reaction. Maybe this was because the automobile was still a new innovation?
World War II Era
- Due to a lack of aluminum, window shield stickers were used to show vehicle registration during the war era.
1963
- Due to miscommunication that year, the abbreviation “Wash” was used on license plates instead of the full word Washington. Chaos ensued! So much so that legislation was enacted forever banning the use of “Wash” on our state’s license plates. I wish TVW had been in place at the time to capture that passionate floor debate!
More on Specialty Plates
Today our state has 70 different plates, with fees varying depending on the plate. A portion of the fees collected from each specialty plate supports the respective cause. Legislation is needed before a new plate goes into effect.
Texas has the most specialty plates in the country with 360 designs!
Our specialty plates focus on the following areas:
Universities
Military
Specific organizations (e.g. 4-H)
Parks and the environment
Sports teams
Tribal groups
Visit the Department of Licensing website if you would like additional information on specialty plates.
Sources: Danny’s License Plates, Washington State Department of Licensing, University of Washington
More Like This
Contact Us
Connect with our team to learn more about our work or discuss how we can support policy and advocacy work for your organization.
Washington State Hub
Learn more about our work in Washington state and access relevant resources and publications.
Start Early is proud to announce the development and building of Educare Lake County, a state-of-the-art early learning school in Zion, Illinois that will serve 174 children, ages 6 weeks to 5-years-old, and their families. Educare Lake County will be the newest Educare school and the second to be directly operated by Start Early through partnerships with Schreiber Philanthropy and other generous donors, the Office of Head Start, and Lake County community members.
Currently, 66% of children in Lake County do not have access to early childhood programming. Educare Lake County will add to existing efforts to bring early learning resources to the community upon its completion and licensing in late 2027. The school will provide full-day, year-round Head Start and Early Head Start programming in six preschool-age classrooms and nine infant and toddler classrooms. Educare Lake County will also include plenty of space for outdoor play and community gatherings. Our caring and bilingual staff and teachers will further support parents through providing information and guidance on goal setting (for children and the family as a whole), getting access to additional services, joining parent support groups, and applying for leadership roles within the school’s Parent Committee and Policy Council.
Stay Connected
For updates on construction progress, opportunities to provide feedback, and more, check out Educare Lake County’s page.
 Over the past year, Lake County residents and Educare teaching staff have been participating in design sessions and focus groups, helping ensure Educare Lake County is an inviting, warm environment where families know they will have access to programs, services and spaces designed just for them. As the development process continues, there will be more opportunities for families to join in on Educare Lake County’s launch, the most recent being the first community information and engagement session of 2025 held on Monday, March 3 at Zion Central Middle School. We welcomed families’ feedback on the design of several key elements and spaces, providing more information about program eligibility and discussing Educare Lake County’s construction and opening timeline. A recording of the event is now available. Keep an eye out for more ways to get involved!
Over the past year, Lake County residents and Educare teaching staff have been participating in design sessions and focus groups, helping ensure Educare Lake County is an inviting, warm environment where families know they will have access to programs, services and spaces designed just for them. As the development process continues, there will be more opportunities for families to join in on Educare Lake County’s launch, the most recent being the first community information and engagement session of 2025 held on Monday, March 3 at Zion Central Middle School. We welcomed families’ feedback on the design of several key elements and spaces, providing more information about program eligibility and discussing Educare Lake County’s construction and opening timeline. A recording of the event is now available. Keep an eye out for more ways to get involved!
Start Early is excited to continue building bridges with Lake County’s early childhood education providers.
We are looking forward to this next phase of the Educare Lake County project and invite you to stay up-to-date on our progress by following us on Facebook and checking our Educare Lake County page for upcoming events and opportunities!

Despite the devastating delays thousands of families across Illinois are experiencing when trying to access the Early Intervention (EI) services they are legally entitled to receive, Governor JB Pritzker’s Fiscal Year 2026 budget proposal does not include any additional state funds for the EI program, which provides critical services to infants and toddlers who have or are at risk for significant developmental delays and disabilities. Instead, the administration is recommending a small rate increase for providers at a cost of $10 million supported by Medicaid funds. While we applaud IDHS and HFS for ensuring we are maximizing Medicaid funds, the funding increase is not nearly enough to address the historically high service delays and long waitlists that are directly tied to the workforce shortage.
The proposal to flat fund EI is concerning and a departure from the multi-year investments announced in 2023 as part of the administration’s Smart Start Illinois initiative, which included a “commitment to regular increases in SFY25-SFY27 on Early Intervention funding mechanisms” following efforts to study and improve EI infrastructure and funding methods. Since then, a cost model study commissioned by IDHS-DEC found that the state needs to raise current spending by an additional $168 million annually to adequately compensate the workforce and stabilize the program. IDHS also invested in cross-state research, which shows that Illinois EI provider reimbursement rates are significantly lower than other states, forcing professionals to leave the field for higher-paying jobs in hospitals, schools, and private practice. These findings underscore a massive funding gap in pay for the workforce and a need for immense investment.
Illinois’ EI program is at a breaking point and the crisis has recently received more media attention than ever before. For the past several months, EI families, providers, doctors and advocates have raised their voices to call for an additional $60 million in the FY26 budget through statewide rallies, 2,200+ petition signatures, and meetings with the Governor’s Office about this issue. It’s time for the state to show their voices have been heard. What will it take for our state to prioritize the needs and rights of infants and toddlers with delays or disabilities and their families? How much more harm will be done before we decide to take action?
Join advocates across the state in calling for a $60 million increase in Early Intervention funding in the FY 2026 Illinois state budget
While the Governor’s proposal does not include an increase in state funding, the Illinois General Assembly has an opportunity to address the EI program’s stubbornly high service delays and workforce crisis. We urge the legislature to increase funding for the EI program by $60 million in the FY26 budget, allowing IDHS to authorize a meaningful rate increase for providers and get closer to the investment needed to stabilize the program. Without additional state funding this year, paired with substantial rate increases, providers will continue to leave the EI program and thousands more children will be denied the services they need. No one wins when we deny these services – the families suffer, developmental outcomes worsen and become costlier to address, and the state places itself at increased risk for the failure to meet its legal obligation to provide services to children and families. The time to act is now. #babiescantwait.
Stay Connected
Stay up to date on early childhood policy issues and how you can take action to ensure more children have access to quality early learning and care in Illinois.
Illinois Policy & Advocacy
For decades, our policy team has been a leading voice and advocate for early learning and care in Illinois.
Contact Us
Connect with our team to learn more about our work or discuss how we can support policy and advocacy work for your organization.
Trish Dauer’s path to nursing and home visiting wasn’t a straightforward one. With a natural inclination toward the human-centered aspects of healthcare, her journey was defined by exploration, adaptability, and a deep passion for connecting with people during critical moments in their lives.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive the latest early learning program and policy news in Washington state.
Discovering a Passion for Connection
“I never set out to be a nurse,” Trish recalls. “In high school, I thought journalism or broadcasting might be my calling—I loved storytelling and learning about people. But as soon as I realized that public speaking made me queasy, I knew I had to rethink my plans.” She shared that her parents’ careers had also influenced her more than she had initially realized. “My dad was a firefighter, and my mom had started nursing school before shifting paths. Healthcare had always been in the background of my life, even if I hadn’t acknowledged it yet.”
A defining moment came when Trish had the opportunity to shadow a nurse practitioner in high school. It was a light bulb moment as she saw how science met human connection. “That experience cemented my decision, and I was determined to pursue nursing despite the daunting competition. I remember being told, ‘You need at least a 3.5 GPA to even apply.’ That was intimidating, but it didn’t deter me. I had found my path, and I was ready to fight for it.”
I realized what I loved most was the deep conversations—the moments when people really opened up.
Trish Dauer, State Nurse Consultant, Nurse Family Partnership Washington
The Shift to Public Health and Home Visiting
Originally thinking she might want to be a labor and delivery nurse, one uninspiring instructor quickly changed that plan for Trish. “I realized what I loved most was the deep conversations—the moments when people really opened up.” That led her to adolescent psychiatric nursing. “My first job at an adolescent psychiatric facility was intense—I was barely 23 and suddenly in charge of a unit. But it was also where I learned how to truly listen. I have always been that person who friends came to and talked to about their problems, and I really like teenagers (a lot of people don’t!)” During an internship at Spokane’s Sacred Heart Hospital in the Adolescent Psychiatry unit before nursing school, Trish shared that her natural ability to talk with people about really hard things came easily, and the tough conversations became her strength.

Following nursing school and her first role in a private adolescent psychiatric facility, Trish knew she wanted something more structured. “I wanted somewhere I could grow. I flirted with the idea of emergency medicine but ended up in public health in Snohomish,” where an early supervisor recognized Trish’s ability to engage with people and encouraged her to start conducting home health visits. “Those first home visits were eye-opening. I drove into neighborhoods I’d never been to, stepped into homes where families were just trying to survive, and realized quickly—there’s no script for this job. Every visit was different, every situation unpredictable. I had no background in maternal-child health, but I knew how to talk to people, and that made all the difference. I found myself having some of the hardest but most meaningful conversations of my career—about postpartum depression, domestic struggles, and the weight of new motherhood. It was messy, but it felt like exactly where I was meant to be.”
Despite having no formal maternal-child health experience, she leaned into her strengths, supporting young parents and learning everything else along the way. That’s when she heard about NFP training and the structure and reasons behind home visiting practices seemed to make sense.
Parents can work through their personal struggles while still being present for their babies. We can hold space for both.
Trish Dauer, State Nurse Consultant, Nurse Family Partnership Washington
Finding Her Calling in Nurse-Family Partnership (NFP)
A year into public health, Trish found Nurse-Family Partnership (NFP) and knew she had found her niche. The structured, evidence-based approach felt like the perfect balance of science and human connection. “The training was intense, but I was confident in my ability to connect with young moms and help them navigate their challenges,” Trish reflected. ”Parents can work through their personal struggles while still being present for their babies. We can hold space for both.”
The Evolution of Home Visiting and Leadership
After years as a home visitor, Trish now leads the Nurse Family Partnership model for Washington state. “Leadership in home visiting isn’t easy. Funding is always precarious, and I’ve spent more time than I ever expected fighting to prove the value of this work.” Trish recently testified before Washington’s Senate Ways and Means Committee in support of home visiting and preservation of recent budget adjustments to provide more inclusive funding for home visiting rates. “Home visiting is one of the best investments in preventive healthcare, but it’s still an uphill battle for recognition and stable funding. I’ve seen firsthand how early support changes lives, and I’ll keep fighting for that. This work isn’t about fixing people, it’s about showing them they already have the strength and resources to succeed. Sometimes, all they need is someone to remind them of that.
Washington State Hub
Learn more about our work in Washington state and access relevant resources and publications.
Stay Connected
Stay up to date on early childhood policy issues and home visiting programming in Washington state.
Resources for Professionals
From interactive courses to engaging events, we support educators in building powerful practices that transform teaching and learning.
Home visiting is a powerful tool for supporting families and communities, and the Washington State Home Visiting Core Competencies are an essential tool to support home visitors. The translation of Washington’s Home Visiting Core Competencies into Spanish, Chinese, Somali, and Arabic is a significant step in ensuring that the competencies are accessible to home visitors in the languages they use and prefer.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive the latest early learning program and policy news in Washington state.
“Created by the field, for the field, the core competencies are intended to be a ‘living’ set of resources that meet the needs of the professionals doing this critical work,” explains Cassie Morley, Assistant Director for Home Visiting at Start Early Washington. These core competencies were crafted with deep engagement from the home visiting community, with over 350 professionals helping to shape them, ensuring that they truly reflect the work and values of the field. “Those documents and those ideas really do belong to them,” Cassie emphasizes. “It seems only fitting that we would try our best to make sure they are available in the languages that that group of people reads and speaks and prefers to take in information in.”
Translating the competencies into these four languages was guided by the home visiting field itself, following the same collaborative and inclusive spirit in which they were initially developed.
By making these resources available in multiple languages, we are reaffirming the commitment to ensuring that all home visitors, regardless of linguistic background, can engage fully with the competencies that define their profession.
Cassie Morley, ASSISTANT DIRECTOR OF HOME VISITING, START EARLY WASHINGTON
A Living, Evolving Resource
These core competencies were never meant to be static documents. “They weren’t intended to sit on a shelf and gather dust,” Cassie notes. “They are for use by the people who created them.” Home visitors are encouraged to annotate them, add notes, and continuously reflect on how these competencies apply to their daily work. The process of refining and updating them is intended to be ongoing by design, informed by feedback from the field. Understanding how the competencies are being used will shape future revisions, with the ultimate goal being to ensure that they remain relevant and actionable, supporting home visitors in their mission to strengthen families and communities.
Home Visiting as a Tool for Inclusion
At its heart, home visiting exists to create trusting relationships between home visitors and parents. One of the clearest ways to achieve this mission is by hiring and supporting trusted professionals from within the communities being served. “What is synonymous with quality in home visiting is DIB (Diversity, Inclusion, and Belonging),” Cassie states. “You can’t really pull those things apart.” The translation of the competencies is a direct reflection of this understanding—ensuring that home visitors from diverse backgrounds have the tools they need in the languages they are most comfortable with.
Bringing Core Competencies to Life
With the core competencies now available in multiple languages, the hope is that home visiting teams will actively engage with them. “I absolutely want home visiting programs to take them up, have discussions about them within their teams, and talk about the ideas represented there,” shares Cassie. “If they feel as if the ideas are important, I want home visitors and their supervisors to talk about how they are turning those ideas into action.”
By making the Washington Home Visiting Core Competencies accessible in Spanish, Chinese, Somali, and Arabic, we are not just translating words—we are reinforcing the values of inclusivity, and community-centered care. These competencies are meant to be dynamic, evolving, and, most importantly, used by the very people who shaped them. The more they are discussed, applied, and adapted, the stronger the home visiting field will be in achieving its ultimate mission: empowering families and communities through trusted, culturally responsive support.
Washington State Hub
Learn more about our work in Washington state and access relevant resources and publications.
Stay Connected
Stay up to date on early childhood policy issues and home visiting programming in Washington state.
Resources for Professionals
From interactive courses to engaging events, we support educators in building powerful practices that transform teaching and learning.

One-Third of the Way Through…
(Photo Courtesy: Erica Hallock)
Trivia!
Legislative committee hearings were held in the Legislative Building until which biennium?
Highlights of the Week
Potato Day!

Potato Day!
(Photo Courtesy: Erica Hallock)
Thanks to the Washington State Potato Commission, folks on the campus enjoyed potatoes with all of the fixings on Tuesday of this week. In one word – YUM!
Senate Majority Leader Jamie Pedersen opened the Legislative Democratic Media Availability this week saying everyone was excited for the best day on the calendar and I thought he was going to cite potato day. But, alas, he was talking about the upcoming policy committee cutoff. I was not alone with that thinking because Speaker Laurie Jinkins joked she thought he was referencing the beloved spuds.
Updated Caseload Forecast Numbers Released
On February 14, the Washington State Caseload Forecast Council released updated forecasts for entitlement caseloads ranging from Working Connections Child Care to K-12 enrollment to adult corrections to Medicaid. These updated forecasts reflect changes from the November 2024 forecast and, along with the March 18 Revenue Forecast, will be used to inform the 2025-27 biennial budget. Bottom line up front – the updated caseload forecasts did not show any sweeping changes from the November forecast.
It is important to remember that the caseload forecasts are based on current law and do not take into account potential shifts in caseloads based on pending statutory changes. For example, SHB 1489 (Ormsby) would delay some of the elements of the 2021 Fair Start for Kids Act, including income eligibility expansion and ECEAP entitlement. Because SHB 1489 is not yet law, the caseload forecasts assume the expansion and entitlement as reflected in the Fair Start for Kids Act are still occurring. Should SHB 1489 be enacted, the next caseload forecast would presumably reflect lower caseloads to reflect the statute changes.
Caseload Forecast by Early Learning Program Area: Comparing February 2025 Forecast to November 2024
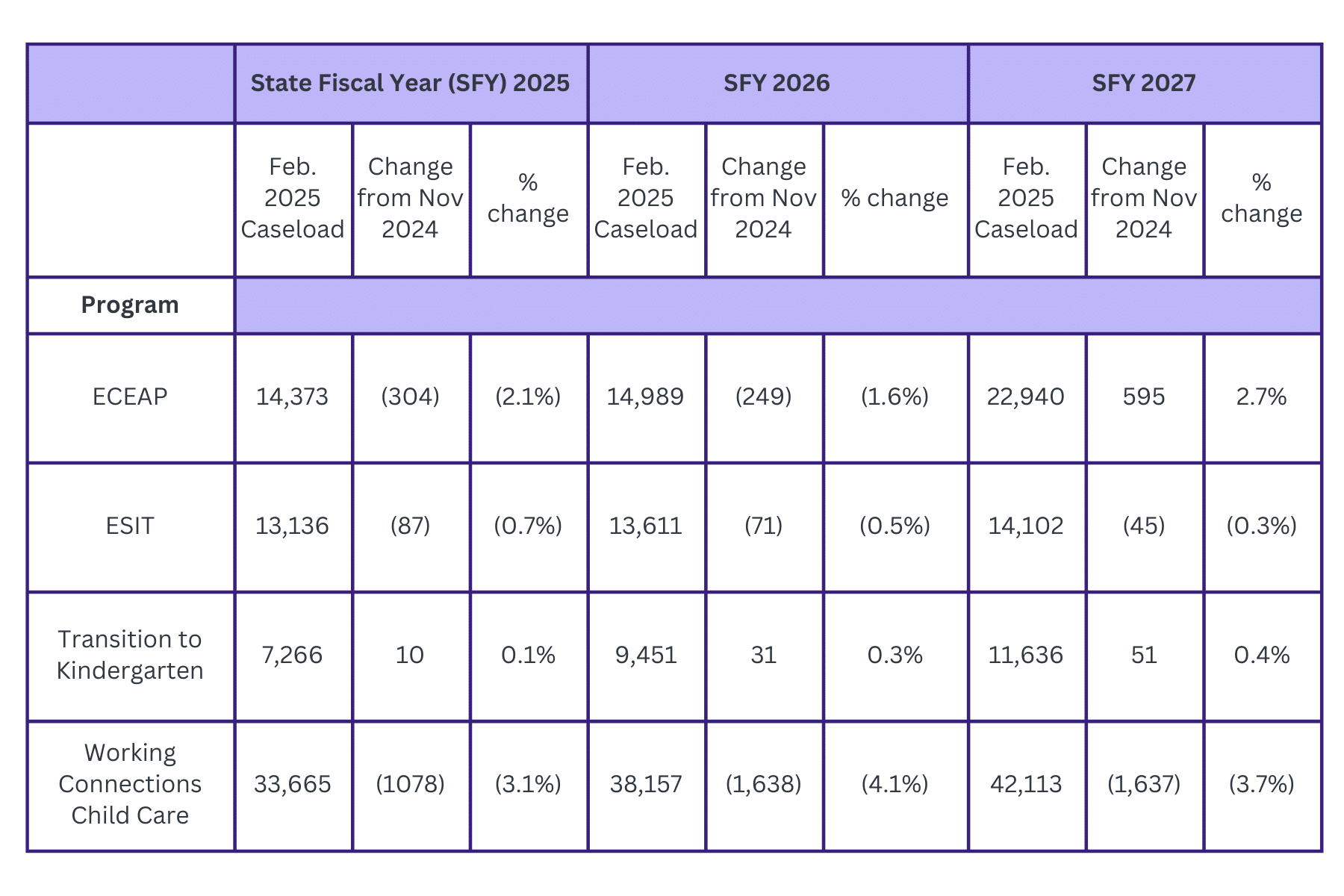
Following take-aways are from the program narratives:
- ECEAP. Actual enrollment is tracking 471 cases, or 3.5%, above the November forecast. Growth in non-entitled enrollment (the program’s largest area of growth in recent years) has slowed since October.
- Transition to Kindergarten. The forecast shows a negligible change from the November forecast. The assumption continues that 135 new classrooms will open each year.
- Working Connections Child Care. Actuals are tracking below the November forecast and the typical summer drop-off was larger than predicted. This is all contributing to the reduced caseload predictions.
Policy Committee Cutoff February 21 – Key Bill Action
As a reminder, each Thursday, Start Early Washington updates its bill tracker with the latest information on bills we are following. As noted last week, we are at the stage in the legislative process where changes can happen quickly so it’s always a good idea to check the legislative website for the latest information.
Executive Action Taken on Provider Qualifications Bill in Policy Committee
On February 17, the House Early Learning and Human Services Committee took executive action on SHB 1648 (Dent) relating to early learning provider qualifications.
The substitute bill adopted in executive session included the following changes:
- Allows licensed early learning providers until at least August 1, 2032 (or five years from the date of hire), whichever is later, to comply with qualification requirements. (The original bill included an extension date of August 1, 2035 or 10 years after date of hire and current law has a deadline of August 1, 2026 or five years after date of hire.)
- Establishes that a provider has demonstrated experience-based competency after working in a licensed child care setting without a break in service for at least five years. (Current rules require seven cumulative years to meet the standard by August 1, 2026. The substitute includes language requiring DCYF to adopt policies to allow for temporary breaks for parental leave, personal or family illness, etc.)
- Requires DCYF to convene a stakeholder group to identify strategies to implement early learning and school-age staff qualification requirements and verification processes and report to the Legislature with recommendations and implementation plans by December 1, 2026.
- Removes the provision in the original bill that would have reset the community-based training pathway to be made available in an online format and instead requires DCYF and the convened stakeholder group to identify options for offering the community-based training pathway in an online format.
Senate Early Learning Facilities Bill Receives Vote in Senate Fiscal Committee
By the time this newsletter hits your inbox, the Senate Ways and Means Committee should have taken executive action on SB 5297 (Trudeau) Thursday evening.
Like its companion, HB 1314 (Callan), SB 5297 would:
- Make Tribal Compact Schools eligible for the Early Learning Facilities (ELF) Public School District grant program.
- Subject to appropriations, establish an emergency grant program for projects that are necessary because of natural disaster or another health or safety threat resulting from unforeseen circumstances.
- Clarify that projects supporting the conversion of Early Childhood Education and Assistance Program (ECEAP) slots to full day and/or extended full day are eligible for ELF Fund grants.
- Remove the level of matching funds as a criterion for selecting projects and make other clarifying changes to matching requirements.
Effort to Revamp Transition to Kindergarten Passes House Education Committee
On February 18, the House Education Committee took executive action on SSB 1450 (Santos) to advance the Chair’s effort to revamp Transition to Kindergarten. The substitute bill adopted in committee struck the contents of the original bill and included the following key provisions:
- Provides that Transition to Kindergarten (TTK) is a policy applying to individual students, rather than a program.
- Defines eligibility as four-year-old children who need an additional year of preparation for kindergarten or live in extreme child care deserts and, despite qualifying, do not have access to ECEAP, Head Start or Working Connections Child Care.
- Beginning in the 2025-26 school year, limits the maximum number of TTK students to the number of students enrolled in the 2023-24 school year. (This would lead to approximately 2,000 less children served in TTK beginning in the 2025-26 school year than currently.)
- Directs that approved TTK sites must be distributed across the state, with areas prioritized that are classified as extreme child care deserts.
- OSPI must adopt an application process for schools interested in providing TTK. Application must include information about the number of sites for which approval is sought and projected number of children served; description of the screening process; statement with supporting documentation whether applicant is located in an extreme child care desert; results of the local child care and early learning needs assessment; and verification from Child Care Aware that the applicant worked in collaboration with and does not adversely impact enrollment in regional early learning programs.
- Requires OSPI to approve schools prior to enrolling students and prior to the school year.
- Requires OSPI to conduct site visits.
Homes for Heroes Bill Receives Public Hearing in House Capital Budget Committee
On February 20, the House Capital Budget Committee held a public hearing on HB 1022 (Connors). Named the “Creating a Home for Heroes Program,” the bill would create a down payment and closing assistance program for people who work in targeted professions and who meet certain income requirements.
Eligible employees include the owner or employee of a licensed or certified child care center, licensed or certified nature-based child care, or licensed family child care home.
Governor Ferguson called out this bill in his inaugural address and said he was excited to work with the bill’s prime sponsor Representative Connors to get the bill to his desk.
Because the House Capital Budget Committee is a fiscal committee, this bill is subject to the February 28 fiscal committee cutoff.
What’s on Deck for Next Week
Fiscal Committee and Other Upcoming Deadlines
Our next cutoff date is coming upon us quickly with the deadline for bills to advance out of Fiscal Committees by Friday, February 28.
Following the February 28 Fiscal Committee cutoff, the next key cutoff date is March 12 – the deadline for bills to be passed out of their House of Origin.
The following week, on March 18, the latest Revenue Forecast will be released. These updated revenue numbers will be used to inform final budget writing.
What Does “NTIB” Mean?
Like the English language, the legislative process has exceptions to its rules. Bills deemed Necessary to Implement the Budget (or NTIB) are exempt from the cutoff deadlines due to budgetary impacts. These bills still must go through each of the steps – they must, for example, receive a Floor vote (no skipping steps!). NTIB status is granted by legislative leadership and is not broadly given.
The reason I share this explanation now is it may appear that some bills are “dead” because they have not advanced through the various policy and fiscal committees by the requisite cutoffs, but they may not actually be dead because they may be deemed NTIB. In short, nothing is ever dead until the final gavel goes down on Sine Die!
Governor Ferguson Expected to Release Next Steps for State Agency Reduction Exercises
As reported in the February 7 “Notes from Olympia,” Governor Bob Ferguson directed state agencies to submit to the Office of Financial Management (OFM) potential budget reductions of at least six percent beyond those reductions included in former Governor Jay Inslee’s public “Book 2” budget.
A February 12 Washington State Standard article reported this exercise would yield approximately $1.8B in savings over the 2025-27 biennium. The article also shared the “cut targets” for state agencies. DCYF’s target was the third largest of the state agencies (note that the Office of Public Instruction was exempt from the exercise) with a two-year reduction goal of $300M. The agency with the largest target was the Department of Social and Health Services with a two-year target of $702.5M and the second largest was the Health Care Authority (the Medicaid administration agency) with $534M.
During a press availability last week focused on Governor Ferguson’s response to the Trump Administration’s actions impacting Washington state, Governor Ferguson addressed the status of this reduction exercise in response to a reporter’s question. Governor Ferguson replied he and his team are actively reviewing the state agency responses and he plans another press availability sometime during the window of February 25-27 to share his administration’s proposed next steps.
Week Seven Schedule
With the policy committee cutoff this week, nearly all the action in week seven will be in the fiscal committees beginning with scheduled Saturday meetings (on February 22) for both the House Appropriations and Senate Ways and Means committees. When next week’s committee schedule came out, it was filled with “bills referred to committee” which are essentially calendar holds. If you are tracking a specific bill carefully, your best bet is to follow the legislative webpage.
Sadly, I am unaware of any scheduled free food days.
Trivia Answer
Committee hearings for a number of legislative committees were held in the Legislative Building as late as the 1975-77 biennium. Who knew that committee hearings used to be held in the Legislative Building? This was news to me! First, I get excited by a free potato and then I get my mind blown by this factoid. I need to get out more…
As I was researching last week’s trivia about the late Senator George Fleming, I came across this 1975-77 Senate Pictorial that included a view into life in the State Senate in the mid-1970s via maps and biographies. It gave me pause about how much has changed in fifty years. A few items that jumped out to me:
- As last week’s Trivia highlighted, there was only one member of color in the State Senate, Senator George Fleming.
- There were only four women Senators – out of 49 total – and “homemaker” was an identified profession.
- To the left of the Rostrum in the Senate, there was a long “press desk” to accommodate the press. Our press corps is not as robust today.
- Senate Pages served for two weeks (now they serve for just five days) and had a dedicated office off of the Senate Floor.
I was fascinated by the maps included at the end of the pictorial and, while they are a bit hard to read, we are reprinting here to highlight some of the changes in the Legislative Building. It is easy to think that an older building has always been situated the way it is today, but these maps demonstrate that is not the case.
And from someone who learned how to type on an old school typewriter, mad props to the typist who got all of this information into these tight spaces. Those are some SKILLS!
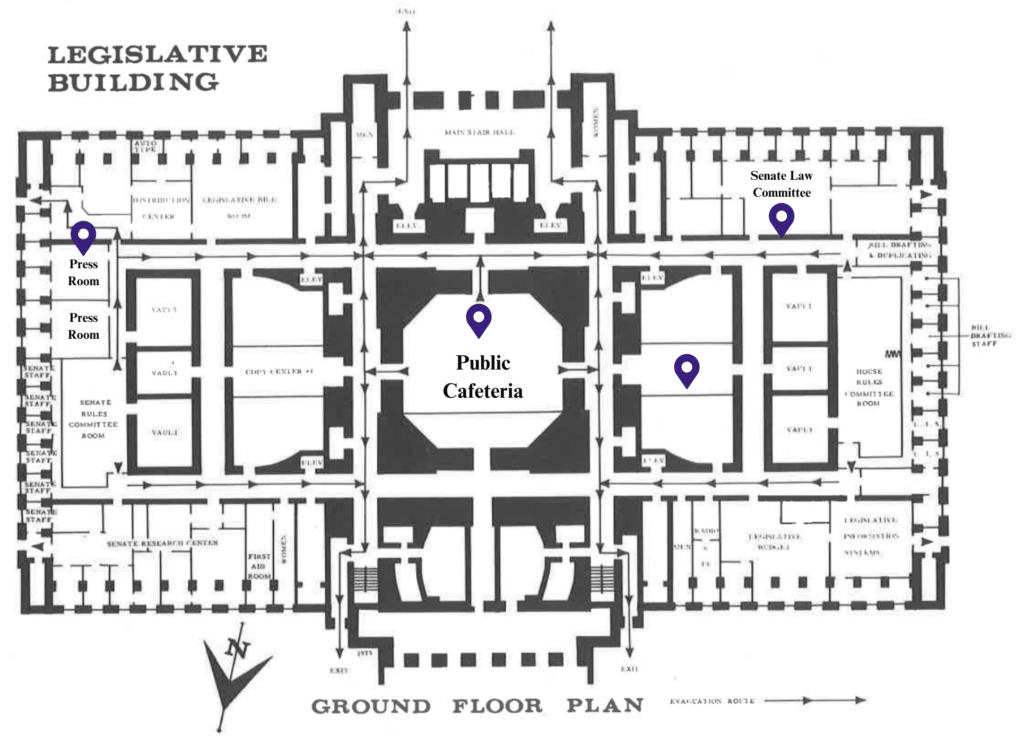
Source: 1975-77 Senate Pictorial
(Map edited for clarity)
- The Public Cafeteria that was in the center of the ground floor is now the Columbia Room which groups can rent out for events/lobby days.
- The empty rooms to the right of the Cafeteria are now the “Dome Deli,” otherwise known as the only place to get food on campus this year!
- The Senate Law Committee space in the upper right is now split into House Republican offices.
- The press rooms on the east side now serve as the gift shop. (I really need to do a trivia on our gift shop – it is a gem!).
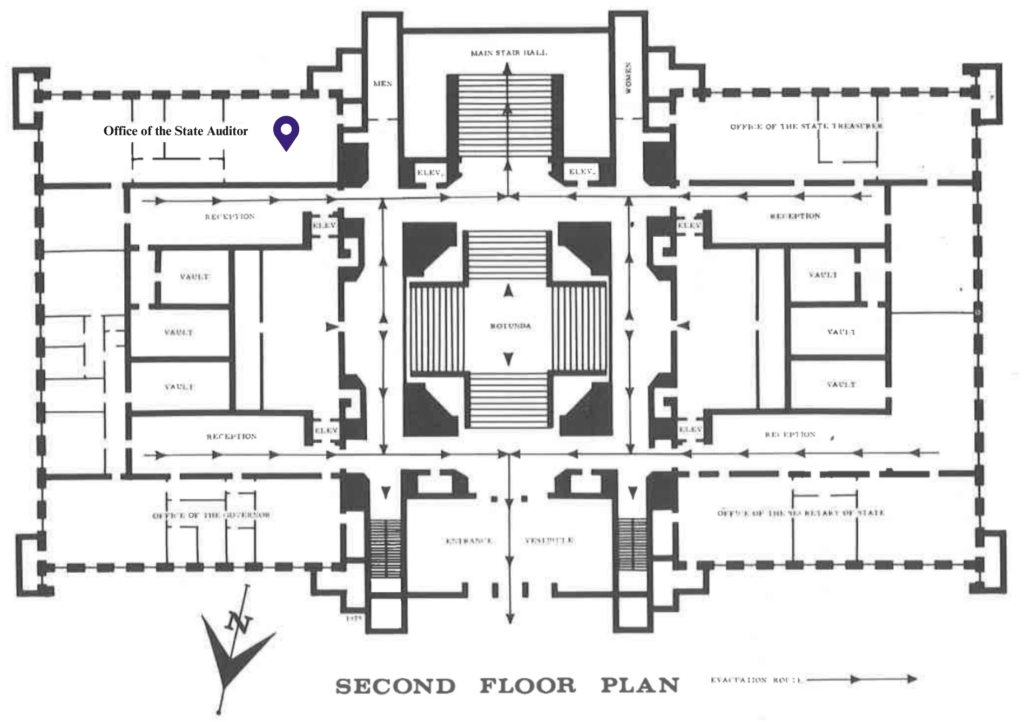
Source: 1975-77 Senate Pictorial
(Map edited for clarity)
- The Office of the State Auditor has since moved to the Insurance Building, which is still on the Capital Campus. The Lt. Governor’s office is now in that space along with the Senate Rules Room.
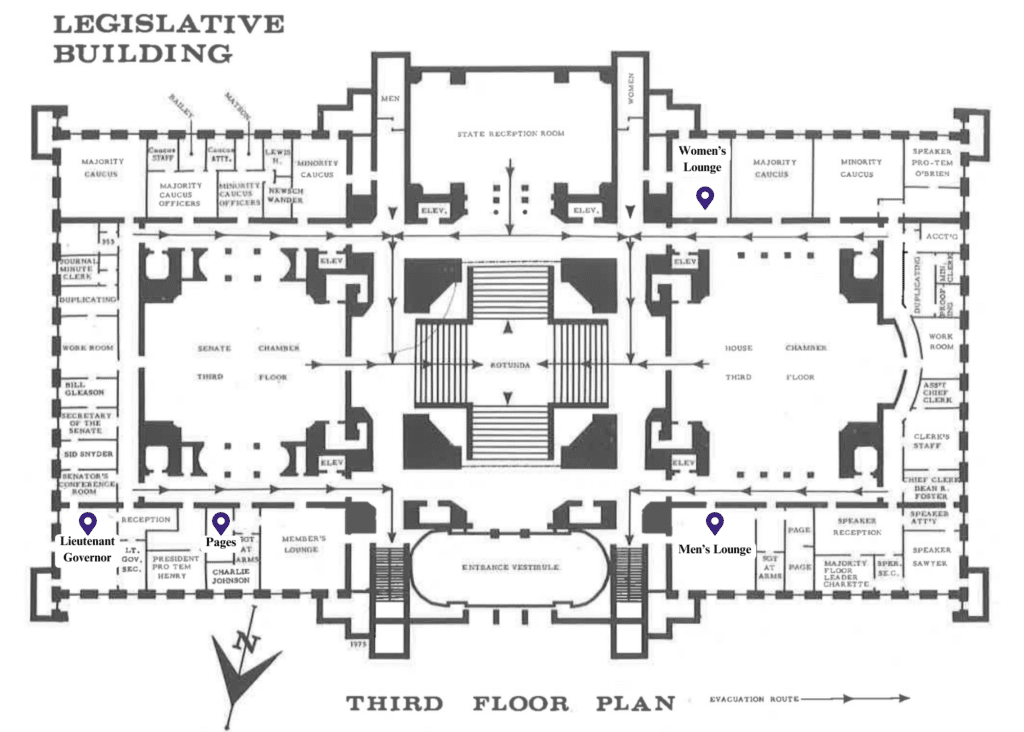
Source: 1975-77 Senate Pictorial
(Map edited for clarity)
- With the Lt. Governor’s office now located on the second Floor, this space in the lower left corner now houses the Senate Majority Leader.
- The Page Room is no longer off of the Senate Floor and the pages do not have a dedicated room in the Legislative Building.
- Check out the size of the Women’s Lounge proportional to the Men’s Lounge. That jumped out to me.
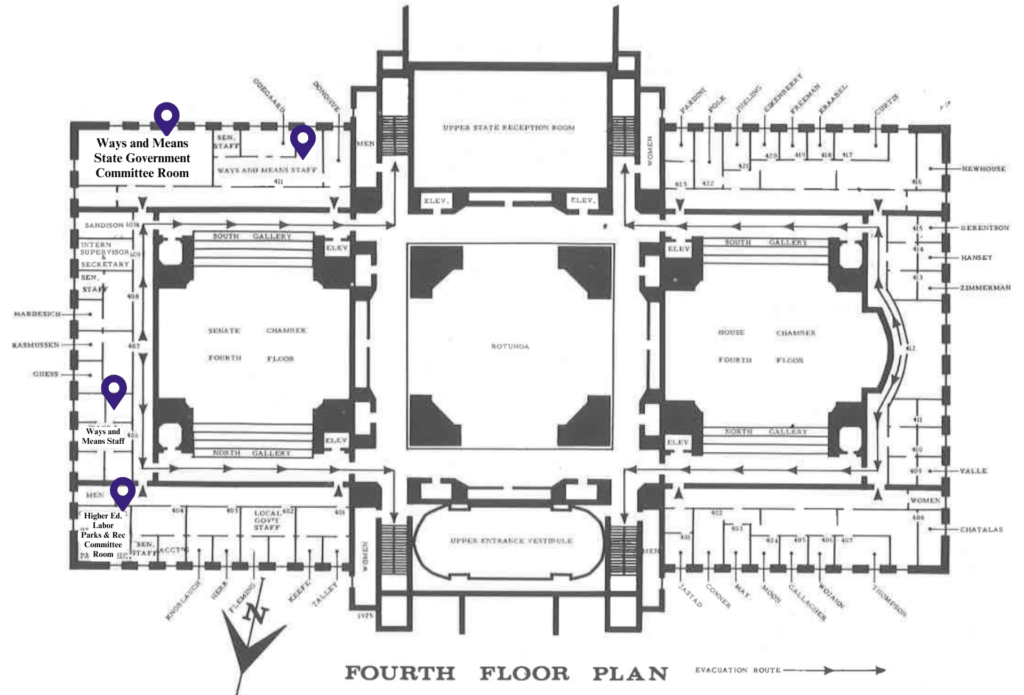
Source: 1975-77 Senate Pictorial
(Map edited for clarity)
- The Fourth Floor on the Senate side is where I see the biggest change. Back in the 1975-77 biennium, this floor held committee rooms for the Ways and Means, State Government, Higher Education, Labor and Parks and Recreation committees. Additionally, there were also offices for the associated committee staff. Today, this area houses legislative offices as well as a page holding area on the Senate side.
- I’m guessing Senators preferred not having to venture out in the rain and snow to go to committee hearings and meet with staff.
I know I missed additional changes. What else did you pick up?
More Like This
Contact Us
Connect with our team to learn more about our work or discuss how we can support policy and advocacy work for your organization.
Washington State Hub
Learn more about our work in Washington state and access relevant resources and publications.
Earlier today, Governor JB Pritzker issued his Fiscal Year 2026 (FY 2026) budget proposal, which outlines considerable funding increases for the state’s child care system, but maintains level funding for its remaining early childhood programs – a departure from the multi-year investments announced in 2023 as part of the administration’s Smart Start Illinois initiative.
Start Early recognizes the state’s financial position, combined with uncertainties in federal funding, made it difficult for the administration to propose significant funding increases across early childhood programs. While we are pleased with the Governor’s request to improve funding for child care assistance ($160 million increase for Child Care Assistance Program; $90 million increase for Smart Start Workforce Grants), the proposal does not provide additional state funds for Early Intervention, evidence-based home visiting programs and the Early Childhood Block Grant (Prevention Initiative and the Preschool for All programs). This lack of investment will limit the state’s ability to support the early childhood workforce and ultimately, to serve more young children through strengthened programs and services.
“We thank Governor Pritzker for his longstanding support for early learning and, particularly, the administration’s decision to prioritize child care access in Illinois,” Start Early Illinois’ Executive Director Celena Sarillo said. “Yet, when we fail to provide sufficient state funding for programs like Early Intervention and home visiting, we fail children during their most crucial developmental periods, and we leave families unsupported in caring for their little ones.”
Take Action on Behalf of Illinois' Children and Families
Ask your legislators to prioritize investments in critical services for our youngest learners.
We are particularly concerned about the proposed budget for the Early Intervention program. The administration is recommending a small rate increase for providers, at a cost of $10 million, which would be supported by Medicaid funds. While this is welcome news, it’s not nearly enough to address record levels of service delays that continue to plague the program – delays linked directly to a shrinking workforce. In fact, earlier this year, the Illinois Department of Human Services released a cost model that found an additional $168 million annually is needed to properly compensate providers and to stabilize the program. Without additional state funding paired with substantial rate increases, therapists will continue to leave the program and more infants and toddlers with or at-risk of disabilities and developmental delays will be left waiting to receive the life-changing services they need and are entitled to by law.
In closing, we thank Governor Pritzker for calling out the risks of federal changes to our state and its communities and for his continued commitment to Illinois’ youngest children and to those who care for them, particularly during such challenging and uncertain times. The child care funding proposed today would preserve recent improvements to provider compensation, address contractually-required rate increases for home child care providers, and allow the state to manage expected caseload growth. It’s a good start, and we stand ready to work with the General Assembly this spring to direct more funding towards the entire early childhood system in Illinois’ final FY 2026 budget. Check out what Start Early will be advocating for this legislative session.
Stay Connected
Stay up to date on early childhood policy issues and how you can take action to ensure more children have access to quality early learning and care in Illinois.
Illinois Policy & Advocacy
For decades, our policy team has been a leading voice and advocate for early learning and care in Illinois.
Contact Us
Connect with our team to learn more about our work or discuss how we can support policy and advocacy work for your organization.

