What is CQI & Why is it Important to Home Visiting?
Continuous Quality Improvement is a reflective, purposeful and systematic approach to support improved outcomes and quality of services for families. CQI promotes learning and curiosity and intentionally creates opportunities for creativity and innovation. By connecting data to practice, CQI helps us analyze systems and root causes to identify and implement meaningful changes.
CQI is an ongoing, collaborative process drawing on expertise and experience at all levels, including home visitors, supervisors, community partners and families. CQI is an essential component of successful implementation within home visiting and other early learning programs. It provides a set of tools to address challenges, promote growth and learning and support adaptations to meet families’ emerging needs and diverse contexts.
How We Support CQI
Through the following activities and their associated benefits, we support home visiting programs in conducting improvement cycles, connecting data to practice and applying CQI tools to support learning and innovation.
- Individual coaching and consultation for home visiting programs provide guidance on program-level improvement projects and support with data analysis.
- Group learning offers programs the opportunity to share and reflect on improvement strategies and learnings.
- Facilitate/liaison connections with national CQI resources and initiatives.
The Basics of CQI
We use the Model for Improvement in our approach to CQI. This is a simple, powerful tool for driving improvement. This model is built around three primary questions:

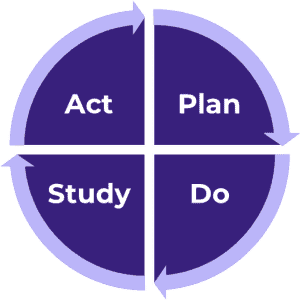 Change takes place through rapid Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles. PDSA cycles are intended to be quick, iterative and reflective. Each PDSA cycle is like a small experiment, supported through thoughtful planning and documentation. PDSA cycles create a meaningful pathway for testing and implementing changes that lead to improvement. Documenting each step of the PDSA cycle is important for learning and disseminating best practices.
Change takes place through rapid Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles. PDSA cycles are intended to be quick, iterative and reflective. Each PDSA cycle is like a small experiment, supported through thoughtful planning and documentation. PDSA cycles create a meaningful pathway for testing and implementing changes that lead to improvement. Documenting each step of the PDSA cycle is important for learning and disseminating best practices.
- Plan. Identify a specific change or strategy (addressing a challenge or area for improvement) to test and create a plan.
- Do. Carry out the plan and collect meaningful data.
- Study. Reflect on results and observations (including any data collected).
- Act. Use learnings to determine next steps (adapt, adopt, abandon).
